In today’s ‘virtual’ world, is any organization immune to the threat of data breaches and cyber attacks? The answer is a big NO. In reality, threats can come to an organization from multiple directions — inside the organization, outside the organization, or a genuine employee’s hacked credentials. In order to identify threats within the organization and to ensure that the organization is in compliance with the federal regulations like PCI and SOX, it is essential to employ Database Activity Monitoring (DAM) as a part of the security and compliance strategy of the organization.
What is DAM?
DAM is a real-time solution that continuously monitors the databases and alerts the organization on recognizing an unauthorized or suspicious activity, and blocks it too. It also helps in investigating database activities that are doubtful in nature. Analytics tools customized according to the needs and environment of a particular organization helps in achieving the desired results.
Functions of DAM
Some of the most common functions of DAM include:
- Real-time monitoring of intra-database attacks as well as backdoors
- Preventing and blocking breaches without being a part of the transactions
- Actively discovering data at risk
- Improving visibility into traffic of applications
- Monitoring database activities even in virtual environments or clouds where consistent and well-defined network topology is absent
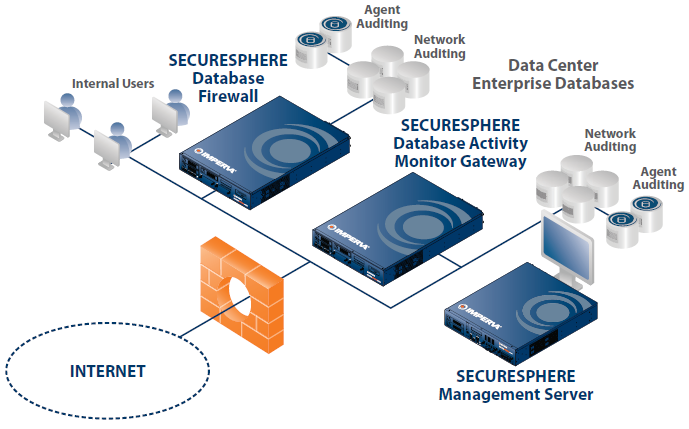
How is DAM Used?
An organization can use a DAM solution in real-time in three different forms:
- Privileged User Monitoring: In this process, the privileged users of an organization like database administrators help desk, developers, system administrators, and outsourced personnel are monitored. They have undisputed access to organizational databases, so it is essential to monitor them in order to provide protection against internal as well as external threats. This process involves auditing all transactions and activities, identifying abnormal activities, and reconciling experimental activities. This helps in ensuring data privacy and data governance.
- Application Activity Monitoring: This helps in increasing the end user accountability to a great extent to detect frauds that happen through organizational applications rather than through direct access to the database.
- Cyber-attack Protection: DAM prevents an SQL injection by monitoring the activity of an application, detects its normal behavior, and identifies the attack in case of divergence from the regular SQL structure and the application’s normal sequence.
Common Architectures of DAM
Following are the three most common architectural forms of DAM tools:
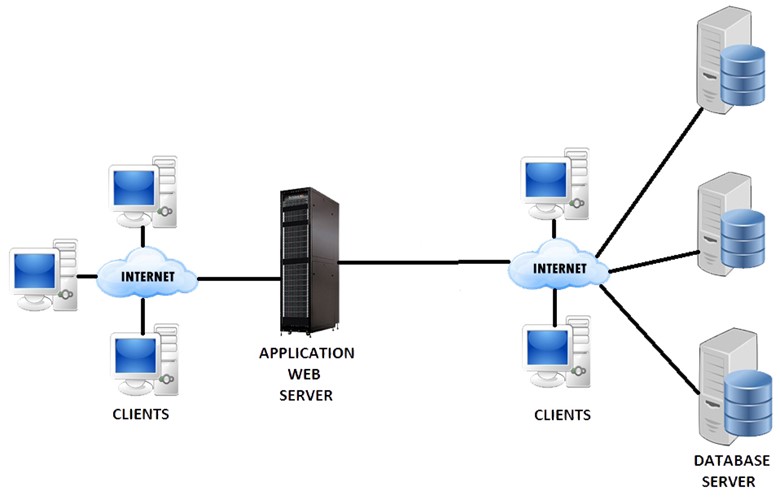
- Based on Interception: Such DAM systems work by ‘looking at’ the communication between the database client and database server. In other words, they monitor the communication stream and get requests and responses from the databases without participating in the whole process. The interception can be done at various points like database memory, network, operating system, or database library.
- Based on Memory: These DAM systems come with lightweight sensors that get attached to protected databases and keeps on monitoring the system global area (SGA) to collect the SQL statements as and when performed. These sensors run on the host and get attached to operating system processes for the purpose of inspecting private data structures.
- Based on Log: Log-based DAM systems extract and analyze information from transaction logs. In case some information is not available in the redo logs, they fetch that data from audit trails. Thus, these systems are a combination of a true DAM system and a security information and event management (SIEM).
DAM solutions are designed to detect cyber attacks and to provide forensic evidence if any data breach happens. These systems enable compliance controls, monitor operations, and provide data protection. While common audit tools help in finding out the data that has been changed, database activity monitoring software helps administrators to gain an insight into who views data and how data is viewed across multiple platforms. To put in a nutshell, DAM aims at differentiating between normal operations and a data breach.