Glioblastoma multiforme is a type of brain tumor that is typically located in the cerebral hemispheres, but can also affect other brain parts. Neoplasm arises from the astrocytes – star-shaped cells that are responsible for brain nutrition, blood-brain barrier formation and repair of the nervous tissue. Glioblastoma can develop both de novo and from the benign astrocytomas. The neoplasm has good blood supply and grows intensively, requiring immediate start of treatment.
Glioblastoma treatment stays in the focus of the international medical society. Thus, in 2019 US National Brain Tumor Society provided 750,000 $ award for launching the first global clinical trial – GBM AGILE (Glioblastoma Adaptive Global Innovative Learning Environment).
Complaints of patients with glioblastoma
Glioblastoma typically arises in patients over 45-50 years old. This brain tumor is rarely diagnosed in children. Definite cause of glioblastoma is still not known. Presence of benign astrocytoma or irradiation of the head and neck region increase risk of the disease.
As the tumor grows fast, it puts pressure on the nearby brain structures and may block cerebrospinal fluid outflow paths. In addition, cerebral tissue around the tumor becomes swollen. That is when first symptoms arise, including:
- Severe headaches that aggravate in the morning and may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Seizures that are resistant to anticonvulsants.
- Blurred vision in absence of ophthalmological disorders.
- Troubles with thinking, speaking, attention focusing.
- Changes in mood or personality, including aggressiveness in localization of tumor in the frontal lobe.
- Weakness or numbness of the extremities.
- Sensory abnormalities in face or/and extremities.
In presence of few symptoms a patient should contact a neurologist for the complete examination.
Procedures for glioblastoma diagnostics
Abovementioned symptoms are not specific exactly for glioblastoma and may be indicative of other neurological pathology. The final diagnosis can be established after the examination:
- Clinical neurological examination includes coordination tests, checking reflexes, estimating muscle strength, etc. It gives basic information about possible cause of worrying symptoms.
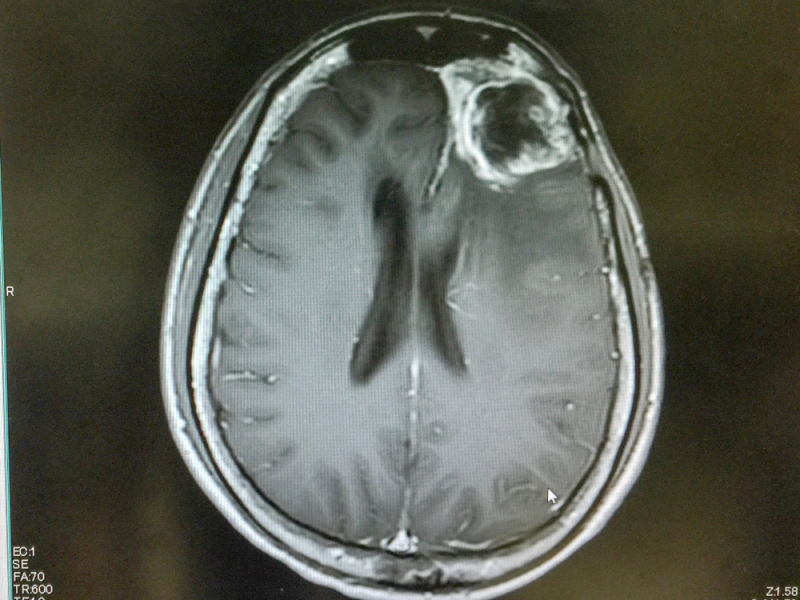
- MRI / CT scan provides a doctor with direct image of the brain tumor and surrounding tissues. Location, size and extent of the glioblastoma spreading become visible.
- Stereotactic biopsy is the neurosurgical intervention during which a part of the tumor is removed for the histological analysis. Stereotactic biopsy needs to be extremely precise in order not to damage healthy cerebral tissue, so it is performed only in best hospitals.
Based on the results of imaging and histological verification, doctor elaborates treatment scheme. Thus, qualitative diagnostics is essential for receiving good therapy outcome.
Treatment of glioblastoma
Due to specifics of glioblastoma, the treatment has several difficulties:
- Presence of blood-brain barrier limits access of many drugs to the tumor.
- Glioblastoma can consist not only of atypical astrocytes, but of other brain cells as well. It is hard to choose treatment that will have the same effect on all types of cells.
- Some treatment techniques can cause brain swelling. This is life-threatening side effect, as volume of the skull is limited and compressed brain may die.
Only limited number of hospitals that have state-of-art technical equipment and highly qualified specialists provide medical services to patients with glioblastoma. Benefits and risks of each treatment type should be carefully estimated:
- Surgical removal of the neoplasm is the best option for radical treatment. The whole tumor is removed if it is not located in the high-risk brain area.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery or MRI-guided laser ablation includes destroying the tumor under the real-time visual guidance. The procedure is less invasive then the conventional surgery and can be performed in patients with hard-to-reach glioblastomas.
- Chemotherapy and immunotherapy (dendritic cell vaccines) slow down tumor growth and boost patient’s own anticancer immunity.
- Radiotherapy and proton therapy consolidate surgery results or may be used instead of it in patients with inoperable tumors.
Neurological rehabilitation is an obligatory part of treatment in leading neurosurgical clinics. Rehabilitation course may last from few weeks to few months, continuing further on the outpatient basis. It helps patients to recover after the operation and restores health back to normal.
Cost of treatment and seeking therapy abroad
Approximate cost of glioblastoma treatment in the best hospitals worldwide is the following:
- Glioblastoma diagnosis – from 1,320 €.
- Surgical removal – from 14,300 €.
- Chemotherapy and radiotherapy – from 22,500 €.
- Neurological rehabilitation – from 640 € per day.
If you want to know prices exactly for your case and investigate details of treatment abroad, you should contact Booking Health. Booking Health is the only certified medical tourism operator that specializes in choosing best hospitals for glioblastoma treatment worldwide. Also, we help in solving all organizational issues of travelling abroad for the medical purposes.
Booking Health assists in making appointment in the most suitable hospital, avoiding overpricing for foreign patients, monitoring medical program at all stages and communication with the clinic after its completion, booking hotels and plane tickets, transfer organization, interpreter services. To start your treatment in the best hospitals abroad you should leave the request on the Booking Health website.




























No Comments
Leave a comment Cancel