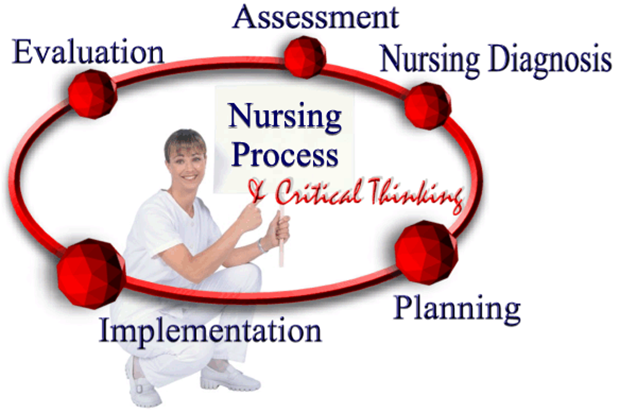
The first stage of the nursing process is a nursing examination
It includes assessing the patient’s condition, collecting and analyzing subjective and objective health data before performing nursing interventions. At this stage, the nurse must:
- Get an idea of the patient’s condition before starting any interventions.
- Determine the possibility of self-patient.
- Establish effective communication with the patient.
- Discuss with the patient the care needs and expected results.
- Fill in the nursing documentation.
The nurse gets subjective data about the patient’s health during the conversation. These data depend on the patient’s condition and his response to the environment. Objective data do not depend on environmental factors. The quality of the survey and information obtained determines the success of the subsequent stages of the nursing process.
The second stage of the nursing process is the definition of nursing problems
Nursing diagnosis is a description of the patient’s condition, established as a result of a nursing examination and requiring intervention by the nurse. Nursing diagnosis is aimed at revealing the patient’s reactions in connection with the disease, can often vary depending on the body’s reaction to the disease, is associated with the patient’s beliefs about his state of health. The main methods of nursing diagnostics are observation and conversation. Particular attention in nursing diagnostics is given to the establishment of psychological contact. After formulating all nursing diagnoses, the nurse determines their priority, based on the patient’s opinion on the priority of providing assistance to him.
The third stage of the nursing process is setting goals, drawing up a plan for nursing interventions
The patient actively participates in the planning process, the nurse motivates the goals, determines along with the patient the ways to achieve these goals. In doing so, all goals must be realistic and achievable. Have specific deadlines for achieving. When planning goals, it is necessary to take into account the priority of each nursing diagnosis, which may be primary, intermediate or secondary. By run-time, all goals are divided into:
- Short-term (their implementation is carried out within one week, for example, a decrease in body temperature, normalization of the intestine);
- Long-term (to achieve these goals requires a longer time than a week). Goals can correspond to expectations from the treatment received, for example, the absence of dyspnoea with exercise, the stabilization of blood pressure.
In terms of the amount of nursing care, there are such types of nursing interventions as:
- Dependent – the actions of a nurse performed at the doctor’s prescription (written instruction or doctor’s instruction) or under his supervision;
- Independent – the actions of a nurse, which she can perform without the appointment of a doctor, according to her competence, i.e. measurement of body temperature, observation of response to treatment, manipulation of patient care, advice, training;
- Interdependent – the activities of a nurse, performed in collaboration with other health professionals, physicians, physiotherapists. Psychologist, relatives of the patient.
The fourth stage of the nursing process is the implementation of the nursing care plan
The main requirements for this stage are: systematic, coordinating the planned actions; involving the patient and his family in the care process; providing first aid according to the standards of nursing practice, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient; maintenance of documentation, registration of care provided and assistance for assignment help UK.
The fifth stage of the nursing process is the evaluation of the effectiveness of the planned care
The nurse collects, analyses the information, draws conclusions about the patient’s response to care, the possibility of implementing a care plan, and the appearance of new problems. If the goals are achieved and the problem is solved, the nurse notes this in terms of achieving the goal on this issue. If the goal of the nursing process on this issue is not achieved and the patient still needs care, it is necessary to reassess, to identify the cause that prevented the achievement of the goal.
Author Bio
Amanda Cernny is health mentor and caretaker worker in the health center in the United Kingdom. In this article, she elucidates the acknowledgment of the nursing care process practice for service users to the new nursing students. Moreover, she supports students in assignment help UK for their academic career.




























No Comments
Leave a comment Cancel